As we outlined in the previous article, 52% of online Hispanics prefer English, 27% are bilingual, and 21% prefer Spanish. The English and bilingual segments are reaching saturation, while the Spanish segment is driving the growth in the Hispanic online market. As a matter of fact, of the 1.6 million new US Hispanics to come online between April 2005 and April 2006, more than 1.0 million prefer Spanish. These statistics support the first Hispanic online marketing best practice: For marketers looking to target the aggregate U.S. Hispanic online market, it is a best practice to use both English and Spanish.
Using both English and Spanish not only allows you to effectively reach all online U.S. Hispanics, but it also delivers value to this audience. U.S. Hispanics live in a bilingual world, and this reality is manifested online.
A bilingual Website for the U.S. Hispanic market has many advantages for marketers and users alike. First, by providing your site in both languages you are giving consumers the choice of which language they want to interact with your site in. In addition, U.S. Hispanics will compare English-language and Spanish-language Websites to ensure that they are getting the same experience in both. By providing a Hispanic online experience in both English and Spanish, you will send a strong signal to the U.S. Hispanic market that you are investing in them. This investment will be rewarded by loyalty and positive world of mouth, which is especially important online.
For examples of bilingual sites for the U.S. Hispanic market, visit www.comidakraft.com and www.elnavy.com. Both sites feature content in both English and Spanish developed specifically for the U.S. Hispanic market; notice that the English content on the Hispanic sites is different from the English on the general market sites www.kraftfoods.com and www.navy.com.
In addition, some cultural nuances are important to consider when offering a Website in both languages. These include:
• English education: A bilingual site represents a great way for Hispanics to learn English.
• Family bilingualism: Bilingual sites will address the varied language preferences of an entire Hispanic household and allow them to experience your Website, as a family, in English and Spanish.
Now that we have identified the use of both English and Spanish as a best practice in reaching the aggregate Hispanic online market, we will turn to the question of whether to localize Spanish content for the diverse subgroups that make up the U.S. Hispanic market. The market is made of people from many Spanish-speaking countries.
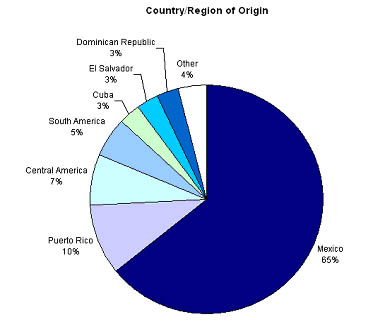 |
| Source: US Census, 2004 |
Effectively communicating with such a diverse population of Spanish speakers is a challenging task. If your strategy is to communicate with the entire U.S. Hispanic market, using a very generic Spanish that avoids colloquialisms–what is commonly referred to as pan-regional Spanish–is the best approach. On the other hand, if your Website is intended for a regional audience you may want to consider using localized Spanish from a specific country. For example, if your company serves only customers in Southern California, using a localized Mexican Spanish may be a good tactic for your Spanish-language site.
When it comes to producing quality Spanish-language content, the best strategy is original Spanish copy written specifically for the Web. This approach will yield the most-relevant Spanish content that has the highest likelihood of connecting with the U.S. Hispanic online market. If budgets do not permit original content development, translation can be used effectively. It is important to work with professional translators who have experience in the U.S. Hispanic online market and expertise in your company’s subject matter. Companies can also employ a hybrid of original content creation and translation, a process commonly referred to as transcreation. Transcreation is the process of taking translated content and adapting to for cultural relevance for the U.S. Hispanic market.
Lee Vann is the cofounder of Captura Group, a leading Hispanic interactive services firm. He was recently recognized by the Interactive Advertising Bureau as one of the top 10 Hispanic online pioneers.
 Network
Network

